To start this guide, download this zip file.
Using pytest
We can see if our code works by running it, but this only shows us that it works for one particular case. To get a better understanding if the functions we have written are working properly, we can write tests for them. One way to do this is with pytest.
Installing the BYU pytest utilities
For CS 110, we have written some libraries that make testing and grading your code easy. We are going to help you install this in Pycharm.
(1) Open PyCharm and select:
- Windows:
File➡️Settings - MacOS:
PyCharm➡️Settings
(2) Select Project and Python Interpreter. The settings/preferences window
should look like this:
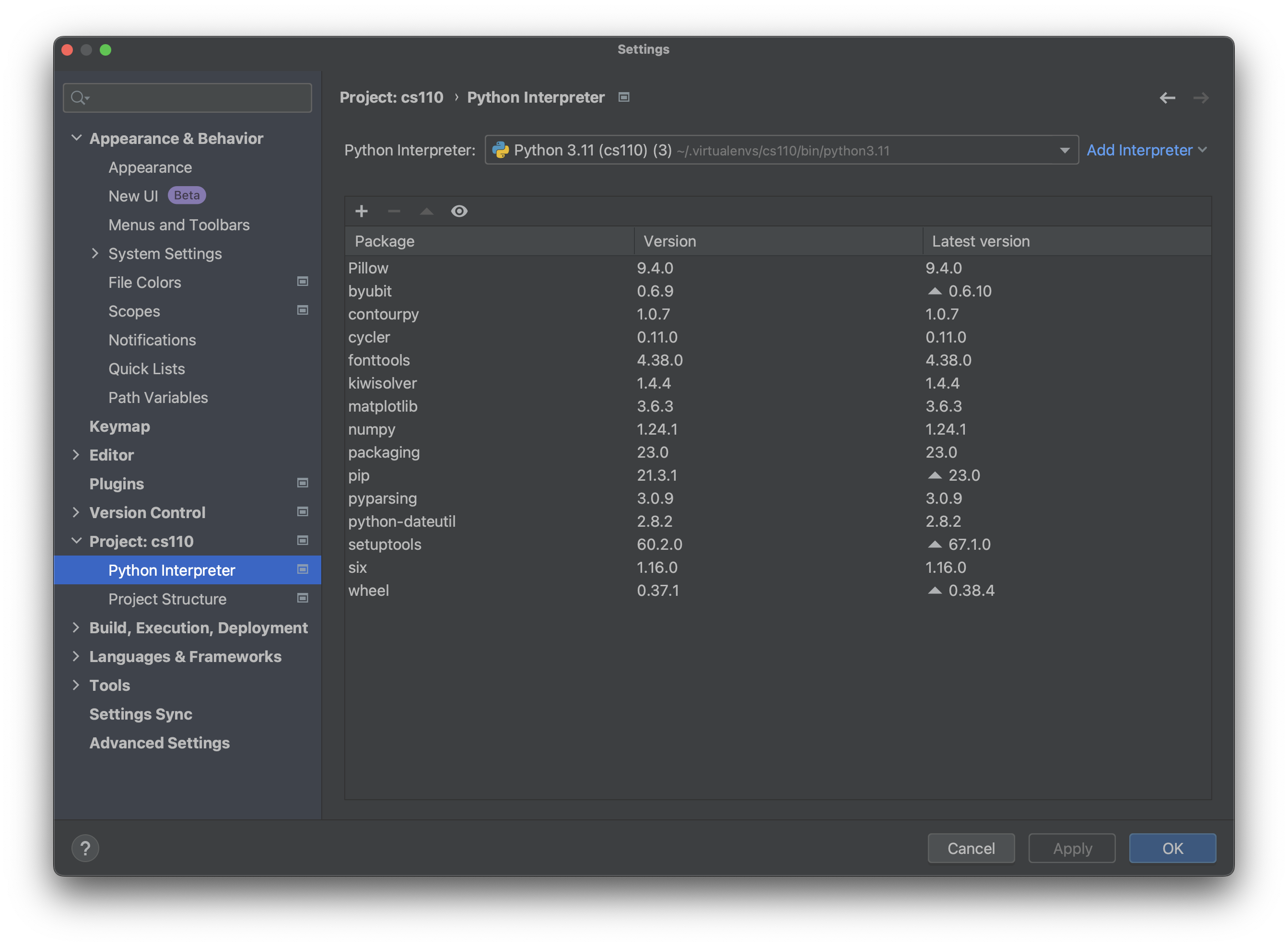
(3) Click on the + sign:
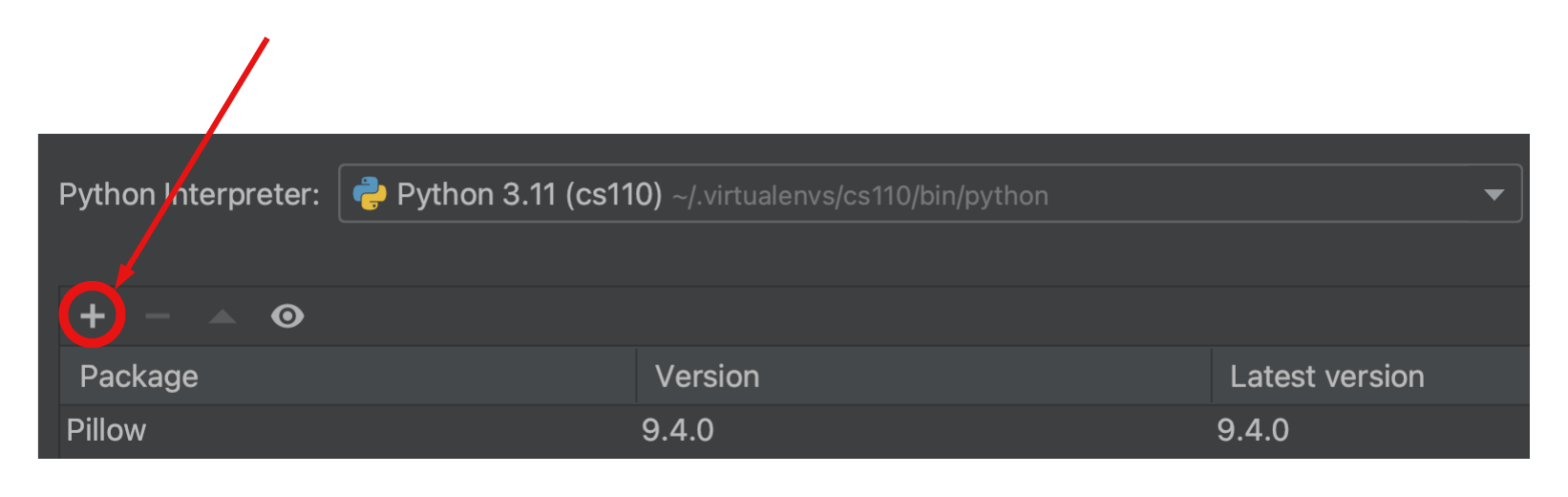
(5) Type byu-pytest-utils into the search box in the new window:
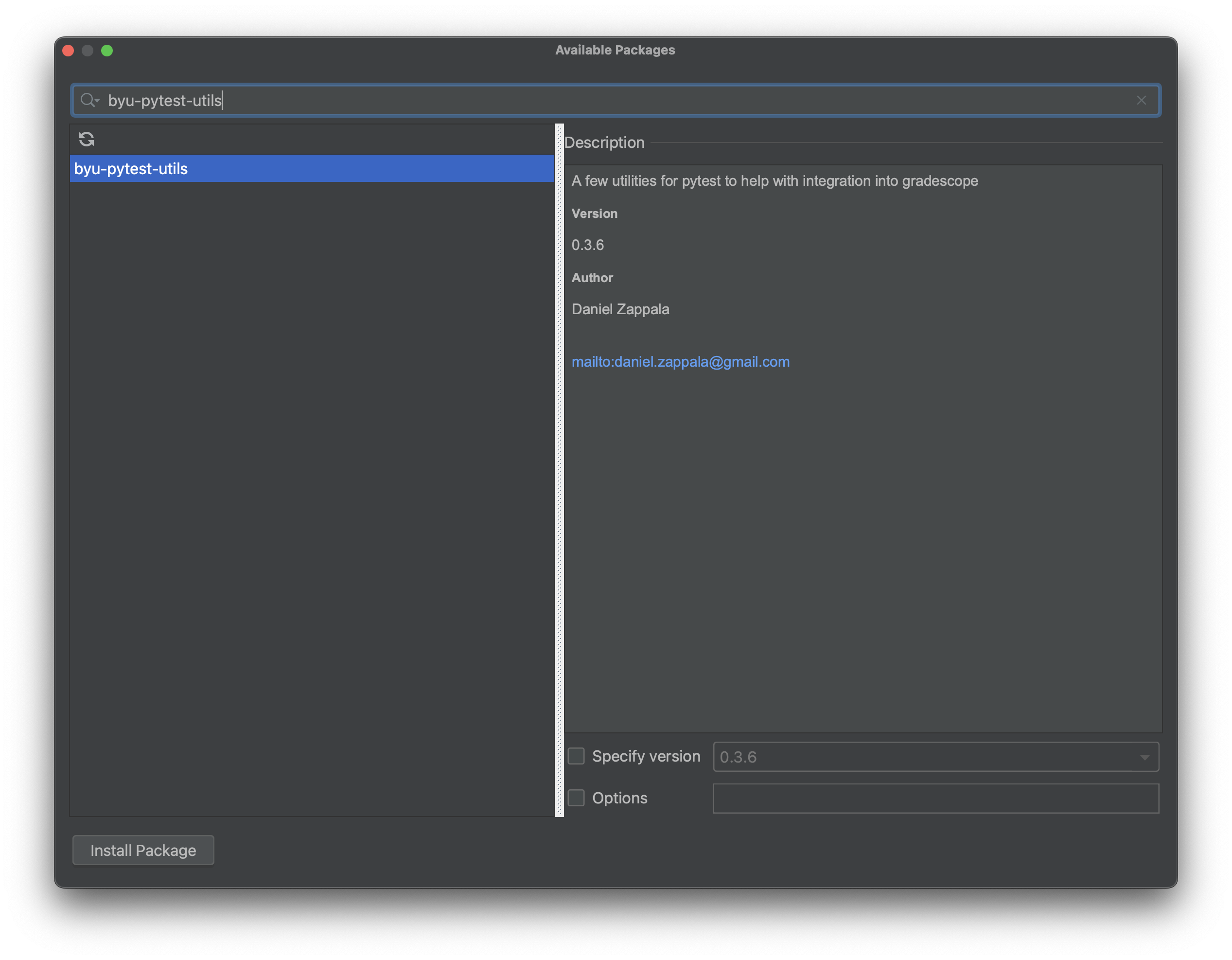
(6) Click the Install Package button. When it is finished installing, close
this window and the settings window.
Setting the pytest runner
Sometimes Pycharm does not recognize pytest as the test runner for your project, and throws an “Empty Suite” error. To prevent this:
(1) In PyCharm and select:
- Windows:
File➡️Settings - MacOS:
PyCharm➡️Settings
(2) In the search box, search for pytest. In the highlighted box, select pytest from the dropdown.
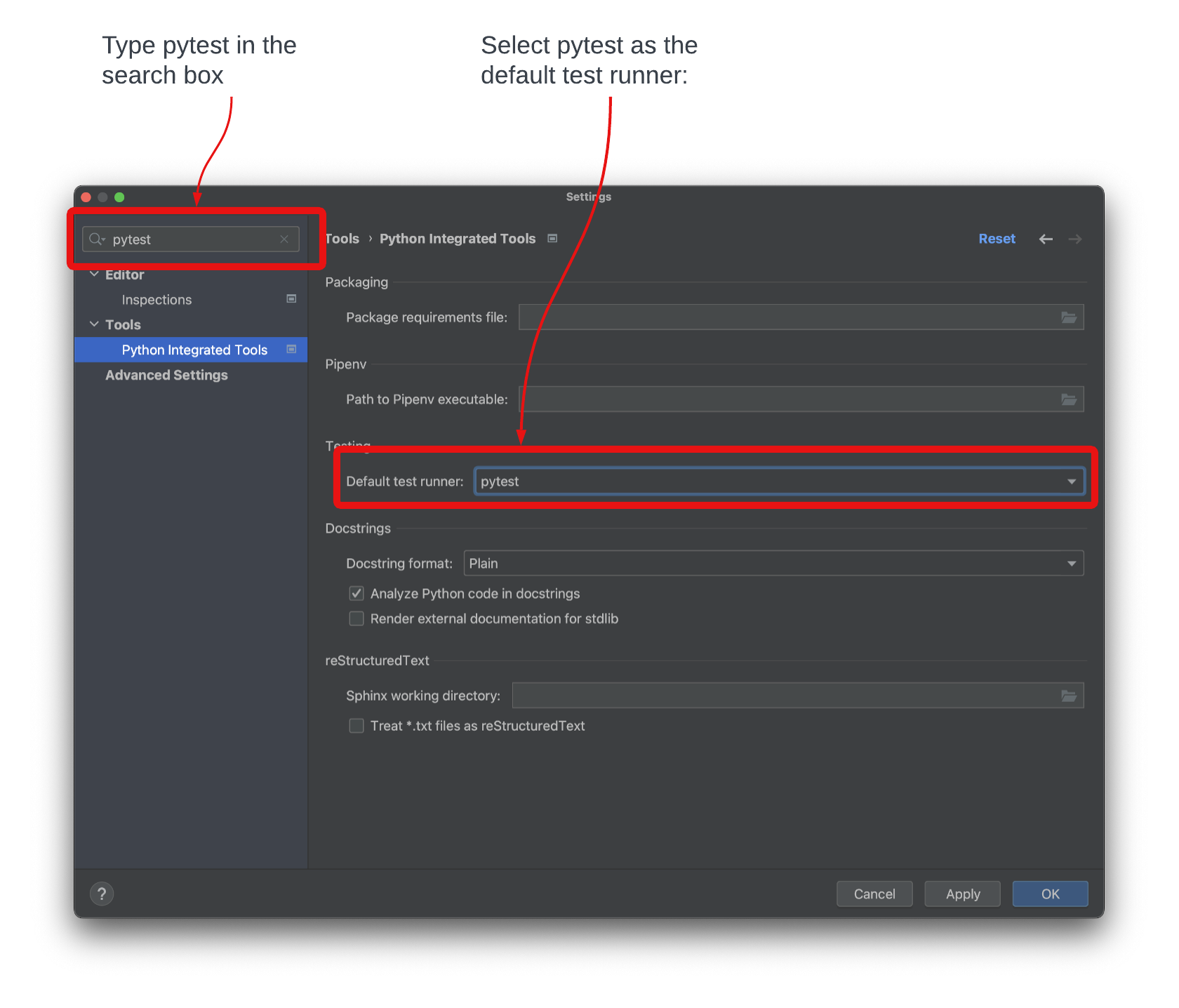
(3) Click OK to close the settings window.
Running pytest
The zip file above contains wendys.py, the program shown in the guide on
interactive programs:
def get_name() -> str:
return input("What is your name? ")
def get_sandwich() -> str:
return input("What kind of sandwich do you want? ")
def get_additions() -> str:
return input("What do you want on it? ")
def print_summary(name: str, sandwich: str, adds: str):
print(f"{name} wants a {sandwich} sandwich with {adds}!")
def main():
print("Welcome to Wendy's!")
name = get_name()
sandwich = get_sandwich()
adds = get_additions()
print_summary(name, sandwich, adds)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()The tests for this program are in test_wendys.py:
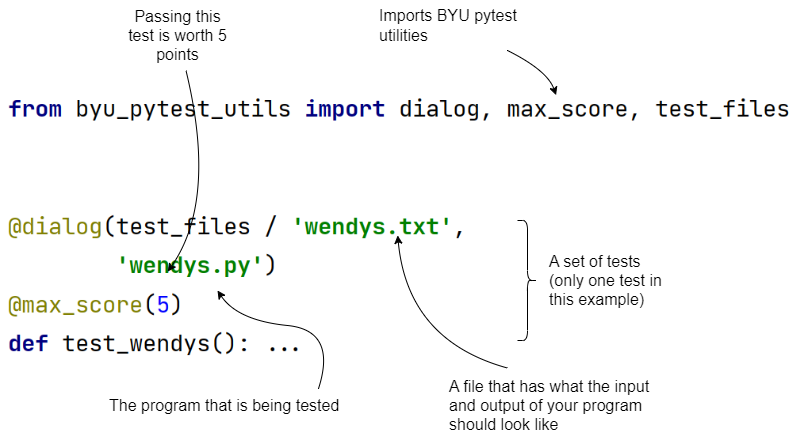
from byu_pytest_utils import dialog, max_score, test_files
@dialog(
test_files / 'wendys.txt',
'wendys.py'
)
@max_score(5)
def test_wendys(): ...The diagram below explains the contents of this file:
Take a look at the file test_files/wendys.txt and this contains the expected
input and output for the test:
Welcome to Wendy's!
What is your name? <<Jorge>>
What kind of sandwich do you want? <<chicken>>
What do you want on it? <<lettuce and tomatoes>>
``Jorge wants a chicken sandwich with lettuce and tomatoes!;output;80``If you read through this, you can see that for this test PyCharm will provide
the following inputs when your program asks calls input():
- Jorge
- chicken
- lettuce and tomatoes
The test expects your program to print out all the output shown. The
dialog() decorator compares the input and output of your program to the
input and output in wendys.txt.
A note on the format of the test file:
- Words surrounded by <<>> are expected inputs.
- Any text surrounded by grave marks is a specific section that pytest will grade, followed by a
;, the name of the test, another;, and the associated grade percentage.
Running tests in PyCharm
To run tests in PyCharm, be sure that both the original file and the test file
are in the same directory and the same folder. In our example, you want to be
sure that wendys.py and test_wendys.py are in the same directory.
When you open test_wendys.py, you should see green triangles next to each test
function:
In this case we have only one test function so there is only one green triangle. In some cases you may see more than one.
You can click the green triangle to run the test and see the output in the lower half of PyCharm:
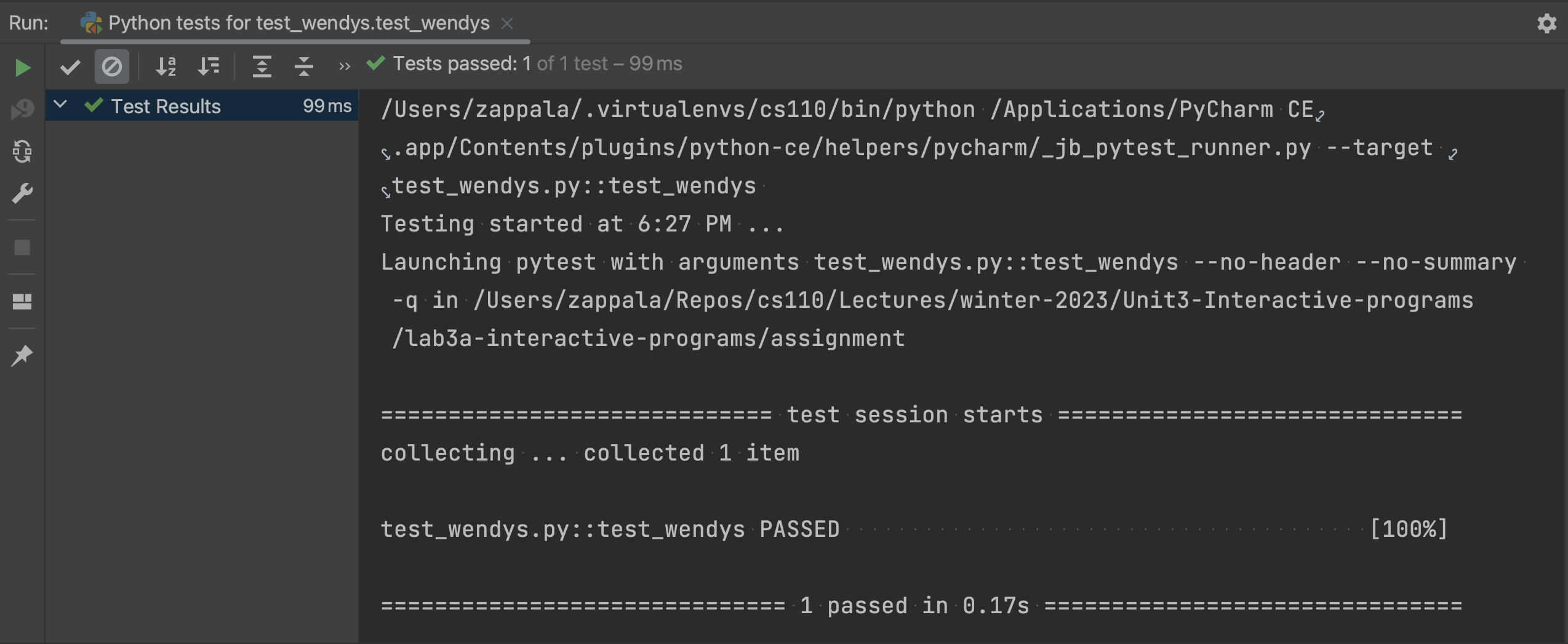
You should see a green check mark on the left, indicating the code passes the test, and also in the screen you will see test_wendys.py::test_wendys PASSED.
An example of a failed test
Modify the code in wendys.py so that the function get_sandwich() reads like
this:
def get_sandwich() -> str:
return input("What kind of bread do you want? ")Notice that we have changed the text of the question. Now go back to
test_wendys.py and run the test again. You should see an error:
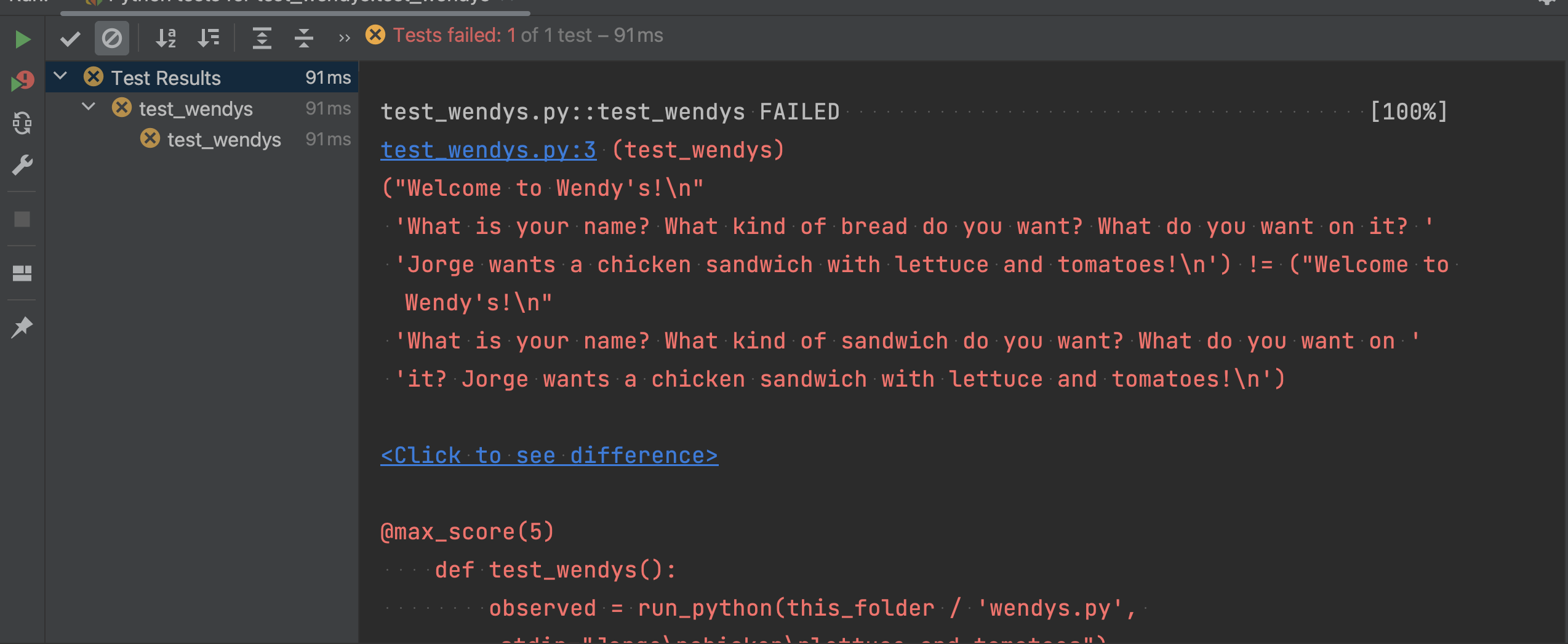
You will see yellow circles with an X on the left, and then errors in red in the
main part of the lower window. The easiest way to see the problem is to click on
Click to see the difference. This will open a new window showing you the
differences between what pytest expected and what your program did:
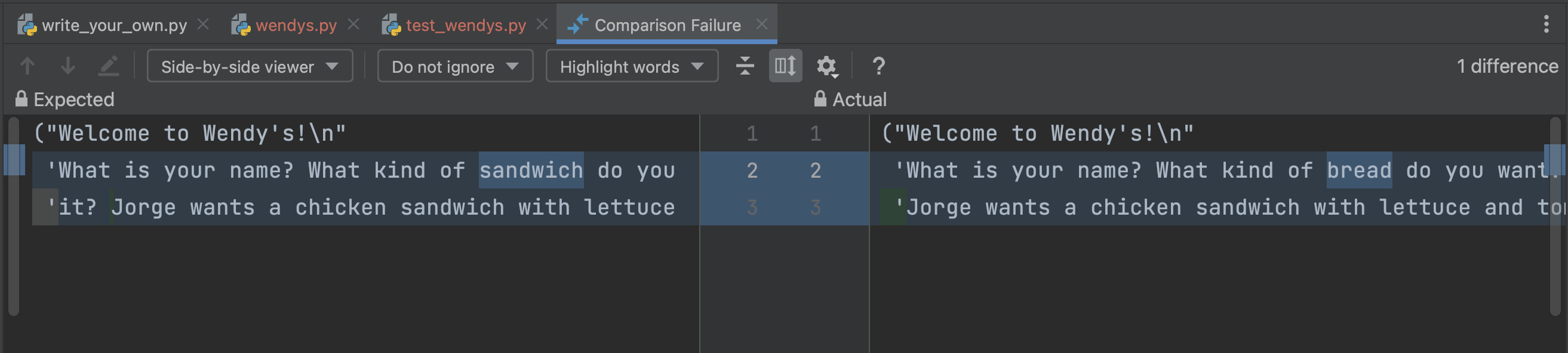
You can see the expected output on the left has the word sandwich highlighted,
and the actual output on the right has the word bread highlighted, showing
where your code has a problem.
Undo your changes to fix the problem, then rerun the tests to be sure they pass.